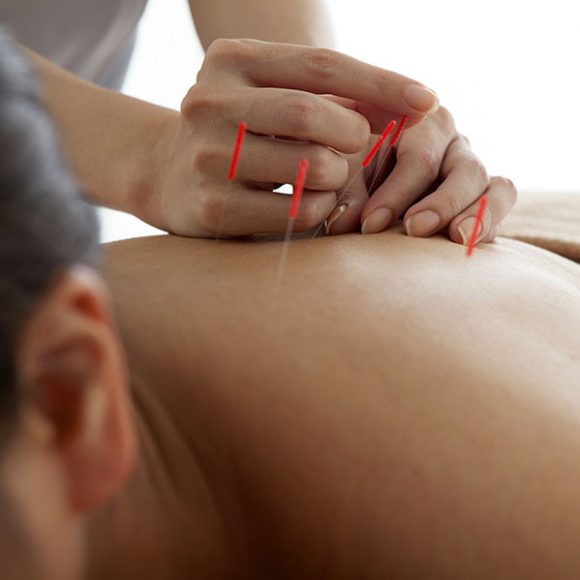
 Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting very thin needles into specific points on the body. It has been well documented in the Chinese medical literature as well as in Western medicine to be an effective modality for pain management. It’s believed to help manage pain through several mechanisms:
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting very thin needles into specific points on the body. It has been well documented in the Chinese medical literature as well as in Western medicine to be an effective modality for pain management. It’s believed to help manage pain through several mechanisms:
- Endorphin Release: Acupuncture can stimulate the body’s natural painkillers, called endorphins. These are chemicals in the brain that reduce pain perception and create a feeling of well-being.
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: It might influence neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a role in mood and pain perception. By modulating these chemicals, acupuncture can help manage pain and improve mood.
- Increased Blood Flow: The insertion of needles may enhance local blood circulation, which can help in reducing inflammation and promoting healing in the affected area.
- Nervous System Modulation: Acupuncture is thought to affect the central nervous system, altering the way the brain and spinal cord process pain signals.
- Immune System Activation: Some research suggests that acupuncture may boost the immune system, which could help in reducing inflammation and aiding the body’s natural healing processes.
- Balancing Energy Flow: In traditional Chinese medicine, pain is often seen as a result of imbalances in the body’s energy flow, or “qi.” (pronounced chi). Acupuncture aims to restore this balance, which is thought to alleviate pain.
While many people find acupuncture helpful for pain management, its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Depending on the length of time a person has been dealing with pain can often influence the number of treatments needed to relieve the problem. With that said, a significant number of people experience a fairly quick reduction in pain and subsequent treatments continue to help reduce and/or eliminate the pain.


Leave a Reply